Crypto futures trading is a derivatives market where you enter into a contract to buy or sell the underlying cryptocurrency at a predetermined price on a specified future date.
Unlike buying cryptocurrency directly, this method allows you to speculate on the price movement of the crypto asset without owning it.
You use margin trading to enter these contracts, meaning you only have to front a fraction of the total value of the trade, known as the margin, to open a position.
This use of leverage can amplify both gains and losses.
A key point of crypto futures is their expiration and settlement – contracts have a set date when they expire, and they settle either in cash or the underlying asset, depending on the specific terms of the contract.
These trading instruments have been integrated into various exchanges, allowing traders like you to gain exposure to cryptocurrencies in a structured and potentially less risky fashion than trading the spot markets.
The purpose of this article is to present a balanced analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of crypto futures trading.
Understanding both facets will assist you in making informed decisions about entering and navigating the futures market.
Pros of Crypto Futures Trading
Leverage: Your trading strategy can benefit significantly from leverage in crypto futures trading. It allows you to control a more prominent position with less capital, amplifying your potential profit on successful trades.
Liquidity: Crypto futures markets often feature high liquidity, ensuring you can enter and exit positions more smoothly. This minimizes the spread costs and makes executing trades at or near your desired price points easier.
Risk Management: Futures can be an effective tool for managing risk in your crypto portfolio. By hedging, you can protect your holdings from adverse price movements and secure profits by locking in prices.
Access: You can access trading opportunities that might not be available in the spot markets. For example, you can short-sell on futures markets, which might be restricted or more complicated in the regular crypto exchanges.
Hedging: If you own cryptocurrencies, you can protect your investments against potential downturns through hedging with futures. This way, losses in your spot holdings can be offset by gains in your futures positions.
Trading Opportunities: Futures trading often comes with an array of trading opportunities and strategies, such as spreading, which can help you benefit from the price differentials across various futures contracts.
Margins: Exchanges offer margin trading, which means you can enter a futures position by putting down only a fraction of the contract’s total value as a margin, increasing your return on investment when the market moves in your favor.
Remember, despite the advantages, it’s essential to consider the risks involved and employ sound risk management practices when engaging in crypto futures trading.
Profit from Market Volatility
In the landscape of crypto futures trading, volatility is a critical concept you can use to your advantage.
Due to the inherent fluctuations in cryptocurrency markets, futures contracts provide opportunities to profit irrespective of the market direction potentially.
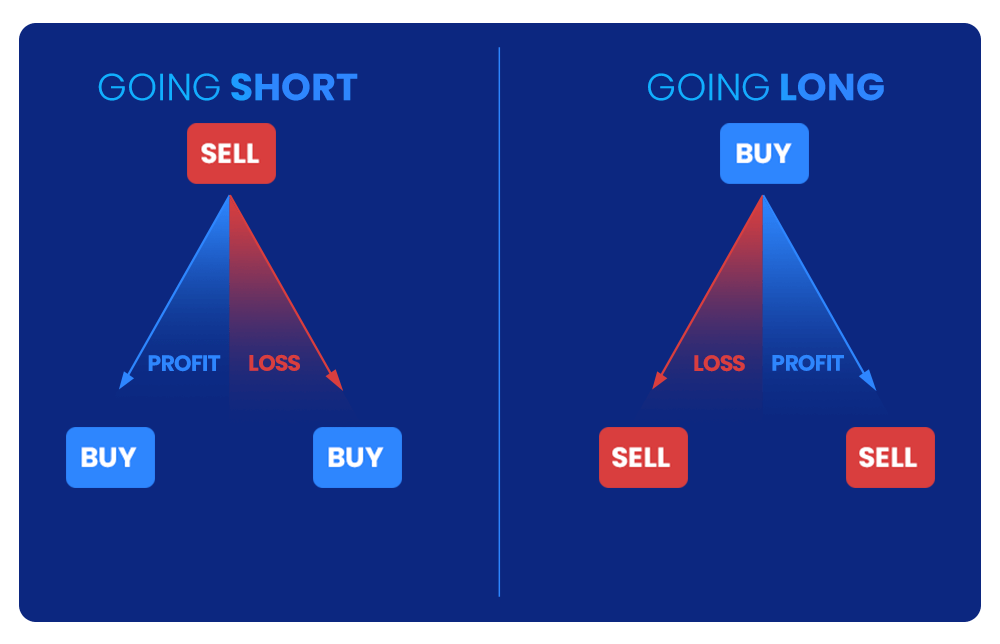
Long Positions: When you anticipate that a cryptocurrency’s price will rise, taking a long position on a futures contract allows you to commit to purchasing the asset at a specific price at a future date. If your prediction is correct and the market price increases, you can sell the contract at a premium before the expiry or settle at a favorable price, thus realizing a profit.
Short Positions: Conversely, if you predict a decline in a cryptocurrency’s price, a brief position enables you to sell a futures contract with the obligation to deliver the asset at a future date. Should the price fall, as you speculated, you can buy back the contract at a lower price, benefiting from the price differential.
Here’s an illustrative example:
- Scenario: The current price of Bitcoin is $30,000.
- Long Position: You enter a futures contract to buy Bitcoin at $30,000, and the price increases to $35,000. You’ve gained $5,000 per contract.
- Short Position: You enter a futures contract to sell Bitcoin at $30,000, and the price drops to $25,000. By buying back the contract, you profit $5,000 per contract.
By strategically entering long or short positions, you can make calculated decisions and potentially profit from the price swings characteristic of the crypto market, no matter which direction the market trends.
Portfolio Hedging
When you trade in volatile markets, such as cryptocurrencies, one of your primary goals may be mitigating price fluctuation risks.
Crypto futures serve as a strategic instrument for this purpose. By entering into a futures contract, you essentially lock in a price for the underlying asset for a future date, which can safeguard your portfolio against the unpredictable nature of crypto markets.
For example, if you hold Bitcoin and anticipate a downturn, you can sell a futures contract at the current price.
If the market price decreases in the future, the gains from your futures position can offset the losses in your spot holdings.
This is akin to taking out an insurance policy for your investments, ensuring that even if the market moves against you, the value of your portfolio remains more stable.
| Advantages | Examples |
|---|---|
| Price certainty | Locking in sale prices for Bitcoin ahead of anticipated drops |
| Risk mitigation | Offsetting potential losses in spot positions during downturns |
| Cost-effective | Utilizing futures as a cheaper alternative to actual selling and rebuying of assets |
Remember that for hedging to work effectively, the size and expiration of your futures contract should correspond closely with your actual crypto holdings.
Properly executed, this technique can provide more predictable revenue streams and reduce the stress associated with price volatility, giving you greater control over your investment outcomes.
Enhanced Liquidity and Access
Crypto futures trading offers you the advantage of increased liquidity.
This is due to the involvement of numerous participants in the market, including retail investors, institutional investors, and market makers.
The consequence is a bustling marketplace where you can quickly enter and exit positions.
Liquidity in Crypto Futures Trading
- Quick Transactions: A high liquidity market ensures you can execute trades promptly. It facilitates timely entry and exit, minimizing the risk of being “stuck” in a position.
- Volume: Trading platforms with high volumes foster increased liquidity. This is vital for your trades, as it indicates a healthy level of trading activity.
- Reduced Spreads: A liquid market typically features lower spreads, which means the difference between the buying and selling price of the futures is minimal. This can reduce potential costs for you.
Accessing the Market
Liquidity also correlates with market access. Crypto futures exchanges operate 24/7, offering you the flexibility to trade according to your schedule, unlike traditional markets with set trading hours.
Furthermore, these exchanges often come with tools and platforms that grant you a broad spectrum of trading capabilities from anywhere in the world.
Examples of Enhanced Liquidity
- Major Exchanges: Platforms like Bybit, Binance Futures, and CME Group provide robust liquidity pools. You will likely swiftly find a counterparty for your trade on these exchanges.
- Market Depth: You can gauge liquidity through market depth, which shows the volume of buy and sell orders at different price levels.
By engaging with established crypto futures exchanges or brokers, you reap the benefits of their high volume and tight spreads.
Always remember to perform due diligence when choosing a trading platform to ensure it meets your requirements for liquidity and access.
Leverage and Margin Trading
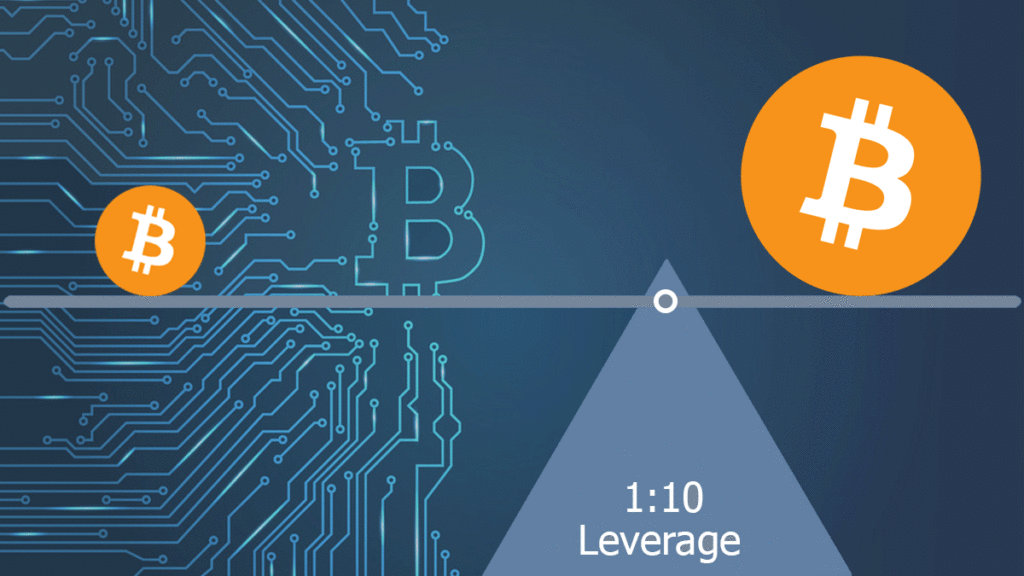
When engaging in crypto futures trading, leveraging and margin trading are crucial concepts to understand. Leverage allows you to control a more prominent position than your existing capital would permit.
By borrowing funds from a broker or exchange, you amplify your trading power, thereby increasing potential returns on investment.
Usually, this is expressed as a ratio, such as 1:10, which means that with $1,000, you could hold a position worth $10,000.
This borrowed money is secured by an initial deposit known as the margin. Consider it as the good faith deposit necessary to maintain open positions.
Here’s a quick look at how margin works:
- Initial Margin: The percentage of the position’s total value you must deposit. If the margin rate is 10%, for a position worth $10,000, you need $1,000 in your account.
- Maintenance Margin: The minimum amount of equity to keep the trade open. If your account balance falls below this, you’ll be subject to a margin call.
Advantages:
- Higher Profit Potential: Even a slight market movement can result in substantial returns with leverage.
- Capital Efficiency: You utilize less capital for more significant exposure, freeing up your funds for other trades.
Disadvantages:
- Amplified Losses: Just as profits can increase, losses can balloon. A small adverse price move can result in substantial losses relative to your initial margin.
- Margin Calls: If the market moves against your position and your balance drops below the maintenance margin, you must quickly add funds or close positions.
Leverage and margin trading in crypto futures can be powerful tools in your trading strategy, but they come with a high-risk level. Use them with an informed strategy and a clear understanding of the risks involved.
Strategic Flexibility and Diverse Instruments
In crypto futures trading, strategic flexibility is paramount. You can select from numerous instruments catering to your risk tolerance and market perspective.
These instruments range from standard futures to more exotic options, each with its mechanics and payoffs.
For example, standard futures contracts allow you to hedge positions or speculate on the future price of a cryptocurrency at a predetermined date.
Meanwhile, options on futures offer the choice to buy or sell the underlying asset at a set price before the contract expires, potentially capping losses while maintaining unlimited upside.
Let’s look at the benefits strategic flexibility offers:
- Personalization: You can use contracts of varying sizes, expiry dates, and underlying assets to tailor your trading strategy.
- Diverse Strategies: Access to calls, puts, and futures gives you a vast tactical arsenal. You can take long or short positions or construct complex strategies like straddles or strangles.
Below are some advantages of these diverse instruments:
- Risk Management: You can mitigate risk by choosing the right instrument for the current market condition.
- Leverage: With futures, you can control prominent positions with a relatively small amount of capital.
- Market Access: Regardless of your assumption, you have the means to express your view on the market movements, bullish or bearish.
Your trading experience will be enhanced thanks to the ability to flexibly employ diverse instruments, allowing for sophisticated portfolio management and strategic planning.
Global Market Participation
One of the primary advantages of crypto futures trading is the access it provides you to the global market.
Crypto futures allow you to engage with different cryptocurrencies across various exchanges worldwide. This inclusivity means that opportunities to trade are consistently available whether a market is rising or falling.
Increased Trading Opportunities: Futures are standardized contracts that can be bought and sold on any futures exchange.
You’re not restricted to a local exchange’s hours or rules. Whether in Asia, Europe, or the Americas, you can execute trades 24/7, capitalizing on market movements as they happen globally.
Diversification: By trading in a global market, you can diversify your portfolio across different assets and geographical regions. This can help mitigate risks localized to specific economies or political climates.
- Night and day trading: Futures markets are almost always open, allowing you to operate on your schedule and react to news events in real time.
- Cross-border exposure: Engage with currencies and commodities that are not available or popular in your home country, enhancing your strategy through varied exposure.
Remembering these advantages is pertinent, ensuring you are well-positioned to make informed decisions in crypto futures’ expansive and ever-changing landscape. Access to global markets empowers you with the choice to diversify and the opportunity to optimize your trading strategy.
Cons of Crypto Futures Trading
When you engage in cryptocurrency futures trading, you must recognize the risks and challenges you may face.
- Complexity: Futures can be intricate financial instruments. Understanding their pricing demands significant financial insight, such as the relationship between futures and spot prices.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile. Extreme price swings can rapidly lead to liquidating your position if the market turns against you.
- Liquidation Risk: Leveraging your trades amplifies potential gains but also increases risks. If the margin in your account falls below a certain threshold, you could be subject to automatic liquidation, erasing your position.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Due to ongoing regulatory developments, the legal and tax implications of trading crypto futures are not always straightforward. This uncertainty can pose a risk to you and your investments.
- Trading Fees: Each trade typically incurs a fee. Frequent trading can thus eat into your profits, especially if those fees are high relative to your trade size.
- Counterparty Risk: When you trade futures, you depend on the exchange’s ability to fulfill the contract. This can expose you to counterparty risk in a decentralized and sometimes unregulated environment.
- Ownership: Unlike owning cryptocurrency, futures do not grant you ownership. You are merely speculating on the price movement.
- Tax Implications: Be aware that futures trading gains can be taxable. You’ll need to keep track of these transactions for tax purposes.
In summary, while futures trading in the cryptocurrency market can present profit opportunities, drawbacks like volatility, complexity, and the ever-present risk of liquidation make it imperative that you approach this market cautiously and informally.
Inherent Risks and Complexity

When engaging in crypto futures trading, you must be aware that the nature of this activity bears high inherent risk and presents considerable complexity.
Risk Factors:
- Volatility: Crypto markets are known for sharp price swings, which can significantly affect futures contracts.
- Leverage: Often used in futures trading, it can amplify gains and losses.
- Market Depth: Crypto markets may lack the depth of traditional markets, which can lead to slippage.
Complexity Factors:
- Contract Details: You should understand contract specifics, such as expiration and settlement.
- Regulatory Landscape: The changing regulatory environment can unpredictably impact futures trading.
Examples of Risks:
In 2020, the rapid decline in oil prices demonstrated how market volatility could lead to unprecedented futures prices, even trading negatively. Imagine similar moves in crypto markets, where Bitcoin has seen daily price swings of over 10%, which is not uncommon.
Evidence of Complexity:
Understanding the intricacies of futures contracts takes time; a study by the Financial Conduct Authority found that less experienced crypto futures traders often misunderstand the terms of futures contracts, leading to costly mistakes.
Liquidation and Amplified Losses
When you engage in crypto futures trading, it’s essential to understand the concepts of liquidation and the possibility of amplified losses. This knowledge can help you navigate the risks associated with leverage.
A maintenance margin is required to keep the position open whenever you enter a futures contract.
If the market moves against your position and your balance falls below this margin requirement, you’ll be subject to a margin call, requiring you to add more funds.
Failure to meet this requirement may lead to the liquidation of your position by the exchange to cover the losses, which could be a significant amount if the leverage is high.
Here’s what you need to know about amplified losses:
- Leverage Multiplies Losses: Trading with leverage implies borrowing funds to increase potential returns. However, this can also magnify losses if the market moves unfavorably.
- Price Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is notorious for its volatility. Rapid price fluctuations can result in sudden margin calls or stop-outs.
- Automated Liquidation: Crypto exchanges automatically liquidate positions once they reach the liquidation price, leaving little room for intervention.
- Partial vs Full Liquidation: Depending on the exchange’s policies and your account balance, you might face partial or complete liquidation.
Consider these scenarios:
- Assume you have a futures position with a 10x leverage, and the market moves in the opposite direction by only 10%. This could ultimately erode your margin, leading to the liquidation of your position.
- If the market moves swiftly and sharply against your position, you may not have time to react. The automated system will liquidate your position, possibly resulting in a total loss of your initial margin.
Proper risk management practices, such as using stop-loss orders and limiting leverage, are essential to safeguard your investments in the volatile world of crypto futures.
Trading Costs: Fees and Commissions
When you engage in crypto futures trading, understanding the associated fees and commissions is crucial for managing your investments effectively.
These costs can vary significantly based on the exchange or broker you choose and the type and size of your contract.
Exchanges and Brokers: Each platform has its fee structure, which can include:
- Trading Fees: Charged for executing trades, these are often calculated as a percentage of the trade volume.
- Clearing Fees: These are paid to the entity that manages the clearing and settlement of the trades.
- Data and Platform Fees: Additional costs may be incurred if you require advanced tools or data.
Contract Types and Sizes: Fees can also depend on the contract specifics:
- Standard Contracts: Typically, larger contracts may have lower relative fees.
- Mini/Micro Contracts: Smaller contracts are often accessible to individual traders but might carry higher relative fees.
Examples of Costs:
- Maker vs. Taker Fees: Some exchanges incentivize market-making by offering lower fees for those providing liquidity (makers) than those taking liquidity (takers).
- Tiered Fee Structures: Depending on your trading volume, exchanges might offer reduced fees as your volume increases.
While fees and commissions are inevitable in trading, thorough research and comparing different exchanges and brokers can lead to more informed decisions that potentially minimize these costs.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
When you engage in crypto futures trading, you navigate a complex landscape of legal and regulatory considerations that vary by jurisdiction.
Legal and Tax Implications:
- Jurisdictional Variance: Your legal responsibilities and tax obligations will differ significantly based on where you’re trading from and where the exchange is based.
- Transaction Nature: Whether you’re trading as an individual or on behalf of an entity, you can change your tax reporting requirements.
Example: In the United States, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) treats crypto futures as commodities, which affects taxation differently than if they were considered securities.
Regulation Uncertainty:
- Regulatory Changes: Future regulations can retroactively impact your tax obligations and the legality of your past transactions.
- International Considerations: Difficulties arise when regulations conflict across different nations, possibly affecting trade on global exchanges.
Evidence: As of the date this article was written, regulatory bodies in many countries have not finalized their stance on crypto assets. This leaves a grey area that could expose you to unforeseen legal and tax consequences.
For example, European countries might implement new regulations that could lead to capital gains taxes on your futures trades, which weren’t previously taxed.
Practical Steps:
- Stay informed on local and international regulations.
- Consult with a tax professional familiar with crypto-related laws.
- Keep detailed records of all transactions to comply with potential audits or regulatory changes.
Understanding legal and tax implications and the uncertainties of looming regulations will assist you in making informed decisions in the volatile crypto futures market.
Absence of Direct Ownership
When you engage in crypto futures trading, unlike purchasing cryptocurrency directly, you don’t gain ownership of the actual coins. This detachment from the underlying asset can influence your trading experience and the benefits you may expect.
Control and Access:
By not owning the actual cryptocurrency, you miss out on specific controls. For example:
- Direct use: You cannot use cryptocurrency for transactions or purchases.
- Private keys: You lack access to the private keys and, consequently, direct and secure control over the crypto assets.
Benefits and Rights:
Ownership usually comes with certain benefits that you forego in the futures market:
- Staking rewards: As you don’t hold the actual tokens, you cannot participate in staking programs that offer additional income.
- Voting rights: Many cryptocurrencies provide voting rights concerning the project’s decisions, which you cannot exercise.
- Airdrops and forks: You might miss out on airdrops or benefits from forks granted to actual coin holders.
Risk Implications:
Your exposure is different without direct ownership:
- Counterparty risk: You’re subject to the risks associated with the solvency and policies of the futures platform.
- Price divergence: You might encounter scenarios where future prices can diverge significantly from spot prices due to market sentiment, which doesn’t affect actual holders as much.
Remember that trading crypto futures contracts means speculating on the asset’s price movements without enjoying the same rights and benefits that come with direct ownership.
Counterparty and Exchange Risks
When engaging in crypto futures trading, counterparty, and exchange risks are crucial considerations.
Counterparty risk is the hazard that the other party involved in the futures contract may default on their obligations. This can stem from insolvency, liquidity crises, or outright fraud.
Exchange risks cover the potential systemic issues associated with the trading platform itself. The platform could suffer from security breaches, technical failures, operational mismanagement, or legal and regulatory challenges. These risks could impact your trades and the safety of your funds.
Examples of Counterparty and Exchange Risks:
- In 2014, the Mt. Gox exchange filed for bankruptcy, and many traders lost their funds due to what was later revealed as a security breach combined with mismanagement.
- A technical failure in an exchange’s matching engine could delay the execution of your futures contracts, possibly resulting in financial loss if the market moves against your position.
You must conduct thorough research on the exchanges and their counterparties. Look for exchanges with strong regulatory standing, robust security measures, and transparent operational processes. This can help mitigate some of the risks associated with crypto futures trading.
Risk Mitigation Strategies:
- Use exchanges with a good track record and robust security.
- Diversify across multiple exchanges to reduce exposure.
- Regularly withdraw profits to a secure wallet.
Remember, while the potential for profit in crypto futures is significant, the risks are equally real. Always proceed cautiously and be well-informed about the platforms and entities you trade with.
Price Volatility
In crypto futures trading, price volatility refers to the rapid and significant price changes that cryptocurrencies often undergo.
This market aspect can work to your advantage or detriment, depending on your position and the market’s movement.
One consequence of volatility is the incidence of margin calls. As you trade on margin, significant price swings could rapidly deplete the equity in your account, triggering a demand from your broker for additional funds to maintain your open positions.
Should you fail to meet a margin call, you may face liquidation. Here, your positions are closed involuntarily at the prevailing market price to prevent further losses that could exceed your account balance.
For example, if you hold a long position and the market sharply declines, or vice versa for a short position, liquidation could crystallize substantial losses.
Additionally, price volatility can prompt stop-outs. Assuming you set stop-loss orders to mitigate risk, a volatile market could activate these orders, thus exiting your positions — potentially in an unfavorable market condition and not always at the price you anticipated due to slippage.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Margin Call | A demand for additional capital to sustain positions due to insufficient equity. |
| Liquidation | Forced closure of positions when margin calls aren’t met. |
| Stop-Out | Activation of stop-loss orders due to price hitting a predetermined level. |
| Slippage | Variation between the expected trade price and actual execution price. |
Your risk management strategies must account for these scenarios to effectively navigate the volatile waters of crypto futures trading.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, you’ll find targeted answers to some of the most pressing questions about the advantages and disadvantages of crypto futures trading.
What are the potential benefits of trading in crypto futures?
Crypto futures trading presents several key benefits, such as leveraging your position, which can amplify gains from favorable price movements.
It also offers the flexibility to go long or short, allowing you to profit from rising and falling markets. Additionally, it can provide a hedge against the volatility of spot markets.
How can crypto futures trading impact portfolio diversification?
Trading in crypto futures can be a valuable tool for diversification as it allows you to gain exposure to cryptocurrencies without directly holding the asset.
This means you can potentially reduce risk by spreading your investment across different financial instruments while still capitalizing on the growth and movements of the crypto market.
What are the primary risks associated with trading crypto futures?
The primary risks in trading crypto futures include significant financial loss due to leverage, which can magnify gains and losses.
Market volatility can lead to rapid and substantial price changes. As crypto futures are derivative products, they carry complexities that can increase the risk of miscalculations or misjudgments in trading strategy.
Conclusion
Your due diligence is paramount in evaluating the landscape of crypto futures trading.
This approach offers opportunities for significant gains, with the leverage available in futures markets enabling control over sizeable positions from a relatively small capital outlay.
However, this leverage is a double-edged sword, as it can amplify losses just as it can magnify profits.
Diversification emerges as a clear benefit, permitting you to broaden your investment portfolio beyond conventional spot trading.
Yet, this diversification also introduces complexity and requires understanding different assets and market strategies.
If you speculate correctly on price movements, thecryptocurrency market’s volatility can lead to substantial gains. Going long or short allows you to adapt to market trends.
However, this same volatility can expose you to the risk of rapid capital depletion.
Your success in crypto futures trading is contingent upon a comprehensive grasp of market forces and a well-crafted risk management strategy. Here’s a summary of key points:
- Leverage: Enhances potential gains but increases risk
- Portfolio Diversification: Provides opportunities to explore numerous assets
- Market Adaptability: You can profit from market upswings and downswings
- Volatility: A high-risk factor that can lead to either significant profit or loss
Remember, the onus lies on you to continually educate yourself and remain vigilant in navigating the intricate dynamics of the futures marketplace.
